- Industrial zone, South of Anping Town, Hengshui, Hebei, China.
- sales@hfpetromesh.com
- +86-18931809706
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
lightweight grating
Lightweight Grating Innovations and Applications
In the realm of optics and material science, a fascinating development has emerged in the form of lightweight grating. This technology has garnered significant attention for its potential applications in various fields, such as telecommunications, spectroscopy, and photonics. The combination of lightweight materials with diffraction grating principles offers a promising future for both scientific research and practical applications.
Understanding Lightweight Grating
At its core, a diffraction grating is an optical component that splits light into its component wavelengths. Traditional gratings are often made from heavy materials like glass or metal, which can limit their application in portable devices. Lightweight grating incorporates newer materials and manufacturing techniques, making them not only easier to handle but also more efficient in a variety of environments. Common materials used include plastics, thin films, and advanced composites, which substantially reduce weight without compromising performance.
The reduction in weight opens new avenues for innovation, especially in industries where weight constraints are critical, such as aerospace, automotive, and mobile electronics. From compact spectrometers to high-performance sensors, lightweight grating makes it possible to achieve superior optical performance while maintaining portability and ease of integration.
Manufacturing Techniques
The fabrication of lightweight gratings has evolved significantly in recent years. Traditional methods, such as ruling or etching on glass or metal substrates, have been largely supplemented by modern techniques like nanoimprint lithography, laser direct writing, and polymer-based processes. These advanced manufacturing methods not only allow for the production of various grating patterns with nanometer precision but also support mass production, which is essential for industrial applications.
One of the most remarkable aspects of these techniques is their ability to produce intricate geometries that would be impossible to achieve with older methods. This flexibility enables designers and engineers to create custom gratings tailored to specific wavelengths or applications, enhancing functionality and efficiency.
Applications in Industry
lightweight grating
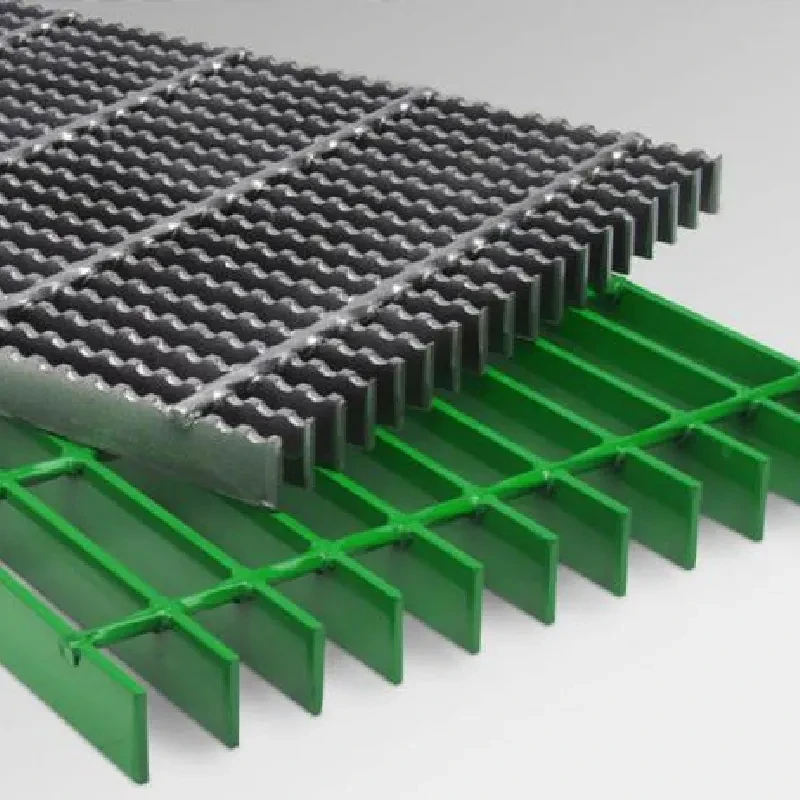
The implications of lightweight grating technology span various sectors. In telecommunications, for example, lightweight optical components are crucial for developing fast and efficient networks. By utilizing lightweight gratings in wavelength division multiplexing systems, data can be transmitted more effectively, leading to faster internet speeds and improved overall performance.
In the field of spectroscopy, portable spectrometers equipped with lightweight gratings facilitate on-site analysis in fields such as environmental monitoring, food safety, and pharmaceuticals. These compact devices allow for rapid measurements without the need for bulky laboratory equipment, making it easier to gather data in remote locations or during field studies.
Furthermore, the integration of lightweight gratings into consumer electronics—such as smartphones and augmented reality devices—opens possibilities for advanced imaging systems. As these devices become increasingly sophisticated, lightweight optics play an essential role in enhancing visual quality while minimizing weight and size.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the numerous advantages of lightweight grating technology, challenges remain. The optical properties of lightweight materials must match or exceed those of traditional components to ensure that performance standards are maintained. Research is ongoing to address issues related to light scattering, thermal stability, and long-term durability.
Furthermore, as industries continue to evolve towards more sustainable practices, the development of eco-friendly materials for lightweight gratings is becoming critical. Innovations in biodegradable polymers and recyclable composites could pave the way for a more sustainable future in optics.
Conclusion
Lightweight grating represents a significant stride forward in optical technology, providing solutions to long-standing challenges associated with traditional diffraction gratings. Its myriad applications across various industries highlight its transformative potential, from enhancing telecommunications to enabling portable spectroscopic analysis. As research progresses and manufacturing techniques improve, the future of lightweight grating is poised to reshape our interaction with light and advance many technological frontiers. Embracing this innovation will lead not only to enhanced optical devices but also to a more connected and capable world.
-
Welded Steel Bar Grating: The Rugged Industrial Flooring Solution Built for Load and LongevityNewsJun.24,2025
-
Steel Walkway Grating: Reliable, Resilient, and Built for Every StepNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shale Shaker Screen for Sale: Optimize Drilling Efficiency with Precision Screening PowerNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shaker Screen for Sale: Elevate Your Drilling Efficiency with Durable Separation SolutionsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Press Locked Steel Grating: Industrial Strength with Precision Fit for Heavy-Duty ApplicationsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Perimeter Safety Netting: The Critical Safety Upgrade for Every HelipadNewsJun.24,2025