- Industrial zone, South of Anping Town, Hengshui, Hebei, China.
- sales@hfpetromesh.com
- +86-18931809706
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Equivalent Weight Calculation for 32x5 Grating Specifications and Performance
Understanding Grating The Importance of Weight in Selection
Grating is an essential component in various industrial and architectural applications, serving multiple functions including safety, drainage, and ventilation. Among the many specifications that need to be considered when selecting grating, weight is a crucial factor that often influences performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. This article focuses on grating, particularly a type referred to as grating 32x5, and examines the significance of its weight in practical applications.
What is Grating 32x5?
The term grating 32x5 typically refers to a specific design of grating where the dimensions indicate the spacing and thickness of the bars 32 mm represents the distance between the bars, while 5 mm indicates the thickness of the bars themselves. This design is commonly used in environments requiring a robust solution for foot traffic or heavy machinery, as it strikes a balance between load-bearing capability and visibility.
The Role of Weight in Grating Selection
Weight plays a critical role in the selection of grating for various applications. Heavier grating options, for instance, generally imply a thicker and more resilient material, which can bear heavier loads. In contrast, lighter grating may be easier to handle and install but could lead to concerns about load capacity and lifespan. The weight of grating not only affects how it is shipped and installed but also its long-term performance in different environments.
1. Load-Bearing Capacity The weight of grating often correlates directly to its ability to support loads. Heavier grating tends to use thicker bars made from stronger materials, which can absorb and dissipate the stress from impacts and weight more effectively. For applications in factories, warehouses, or outdoor platforms, selecting the right weight is vital to prevent structural failure.
grating 32x5 weight
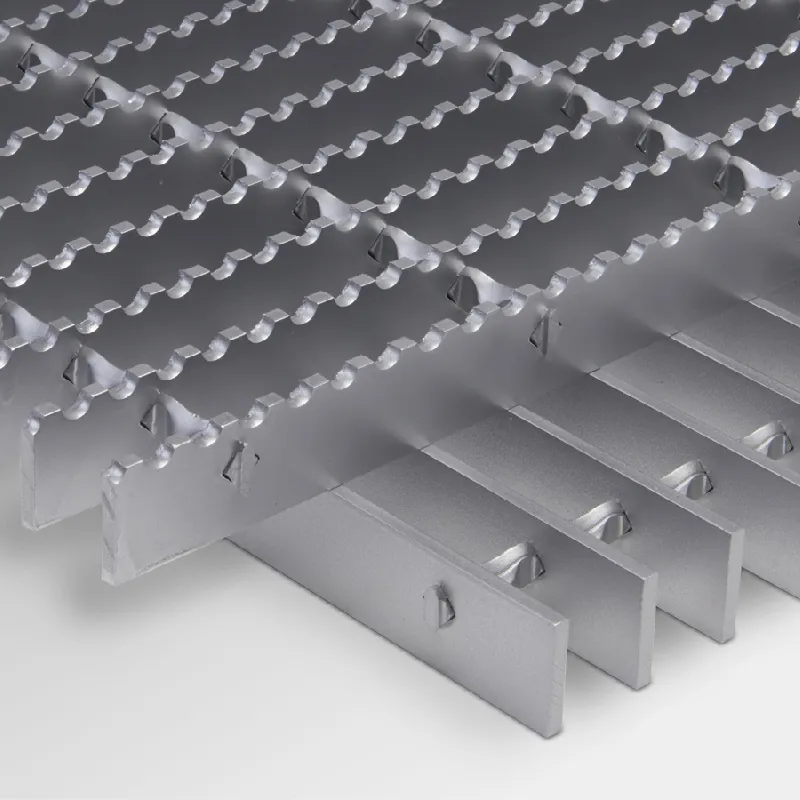
2. Material Choice The type of material used in manufacturing grating significantly influences its weight. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and fiberglass. Steel grating is considerably heavier but offers exceptional strength and longevity, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Aluminum grating, while lighter, provides corrosion resistance and may be preferable in environments exposed to moisture. Fiberglass grating is lightweight and non-corrosive, often utilized in chemical plants and coastal areas but may not match the load-bearing capability of steel.
3. Installation Efficiency The weight of the grating impacts the complexity of installation. Lighter grates can be easier to handle, which potentially reduces labor costs during installation. In contrast, heavy grates may require more manpower or lifting equipment, increasing both time and financial investments.
4. Transportation Costs Weight is an essential consideration in shipping and logistics. Heavier grating means higher transportation costs, which can impact the overall budget of a project. Opting for a lighter yet suitable alternative can help manage these expenses while ensuring compliance with safety and performance standards.
5. Integration with Other Materials In many projects, grating is integrated with other structural components. Understanding the weight of grating can aid in maintaining balance and structural integrity when combined with supports, stairs, or platforms.
Conclusion
In summary, the weight of grating, particularly types like grating 32x5, is a multifaceted aspect that influences various stages of production, installation, and maintenance. As industries evolve and demand materials that are not only strong but also economically feasible, understanding the relationship between weight, capacity, and application becomes increasingly relevant. By carefully considering weight alongside other factors, architects, engineers, and project managers can make informed decisions that enhance both safety and effectiveness in their grating selections.
-
Welded Steel Bar Grating: The Rugged Industrial Flooring Solution Built for Load and LongevityNewsJun.24,2025
-
Steel Walkway Grating: Reliable, Resilient, and Built for Every StepNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shale Shaker Screen for Sale: Optimize Drilling Efficiency with Precision Screening PowerNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shaker Screen for Sale: Elevate Your Drilling Efficiency with Durable Separation SolutionsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Press Locked Steel Grating: Industrial Strength with Precision Fit for Heavy-Duty ApplicationsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Perimeter Safety Netting: The Critical Safety Upgrade for Every HelipadNewsJun.24,2025