- Industrial zone, South of Anping Town, Hengshui, Hebei, China.
- sales@hfpetromesh.com
- +86-18931809706
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
galvanized grating sizes
Understanding Galvanized Grating Sizes
Galvanized grating is a versatile and durable solution widely used in various industrial and commercial applications. It consists of a grid-like structure made from steel bars that are coated with a layer of zinc through the process of galvanization. This coating not only enhances the longevity of the grating by preventing rust and corrosion but also adds to its aesthetic appeal. One crucial aspect of utilizing galvanized grating in projects is understanding the different sizes available and their applications.
The Importance of Grating Sizes
When selecting galvanized grating, size plays a pivotal role. The size of the grating affects both its load-bearing capacity and its applicability to specific projects. Galvanized grating typically comes in various dimensions, including different thicknesses and spacing between the bars. Understanding these dimensions ensures that the right type of grating is chosen for specific loads and environmental conditions.
Common Sizes of Galvanized Grating
Galvanized grating is available in multiple sizes, which can vary based on the manufacturer. Commonly, the standard widths range from 24 inches to 48 inches, while lengths can extend up to 24 feet. The thickness of the bars can vary from 1/8 inch to 3/4 inch, depending on the intended use and load requirements.
The spacing between the bars is another critical factor. Typical spacing options include 1 inch, 1.5 inches, and 2 inches center-to-center. Narrower spacing is often used for applications requiring a smooth surface to prevent objects from falling through, while wider spacing may be acceptable where debris can pass freely, such as in drainage applications.
Load Capacities and Their Implications
Different grating sizes and configurations can support varying load capacities. For instance, heavier and thicker grating can bear more weight, making them suitable for industrial applications like walkways, platforms, and catwalks. On the other hand, lighter grating may be adequate for applications such as ventilation covers or lightweight platforms.
galvanized grating sizes
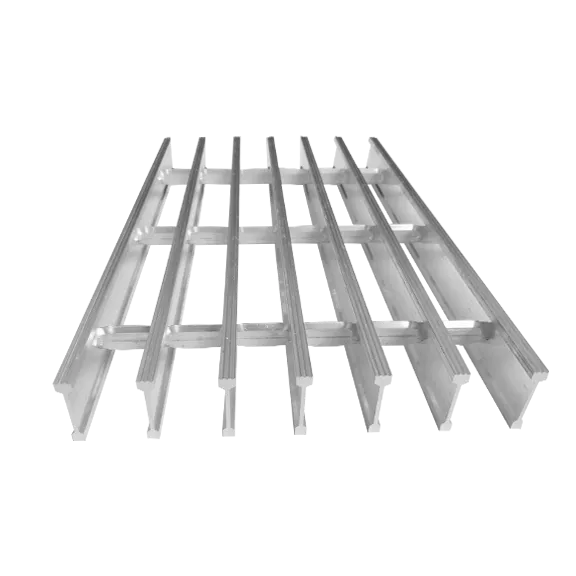
Understanding the load requirements for a specific application is vital. The load capacity is typically influenced not only by the size and thickness of the grating but also by the span—how far it is supported. Accurate calculations must be made to ensure safety and efficiency in design.
Applications of Galvanized Grating
Galvanized grating finds application across various sectors, including construction, manufacturing, food processing, and wastewater treatment. In construction, it is often used for flooring, stair treads, and walkways. In industrial settings, it serves as a platform to facilitate personnel access to machinery and equipment while ensuring safe passage.
Moreover, the food processing industry relies on galvanized grating for cleanliness and hygiene, as its smooth surface is easy to clean and does not retain contaminants. In wastewater treatment, grating allows for efficient drainage while providing structural support for equipment.
Customization and Special Sizes
While standard sizes can accommodate a broad range of needs, many manufacturers offer customized sizing options. Custom sizes are particularly beneficial for unique projects that do not fit standard dimensions. This flexibility is essential for ensuring that the grating meets specific dimensional and load-bearing requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding galvanized grating sizes is vital in selecting the right type for any given application. Various sizes, thicknesses, and spacing options are available, each tailored to meet specific structural and load demands. By assessing the requirements of the project and consulting with manufacturers, architects, and engineers, one can ensure the selection of the appropriate galvanized grating that will not only serve its intended purpose but also provide longevity and safety within the operational environment. As industries continue to evolve, the need for durable, reliable, and customizable solutions like galvanized grating will remain a fundamental aspect of structural design and engineering.
-
Welded Steel Bar Grating: The Rugged Industrial Flooring Solution Built for Load and LongevityNewsJun.24,2025
-
Steel Walkway Grating: Reliable, Resilient, and Built for Every StepNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shale Shaker Screen for Sale: Optimize Drilling Efficiency with Precision Screening PowerNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shaker Screen for Sale: Elevate Your Drilling Efficiency with Durable Separation SolutionsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Press Locked Steel Grating: Industrial Strength with Precision Fit for Heavy-Duty ApplicationsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Perimeter Safety Netting: The Critical Safety Upgrade for Every HelipadNewsJun.24,2025