- Industrial zone, South of Anping Town, Hengshui, Hebei, China.
- sales@hfpetromesh.com
- +86-18931809706
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
ditch cover steel grating
The Role of Ditch Cover Steel Grating in Modern Infrastructure
In the realm of civil engineering and infrastructure development, ditch cover steel grating is an essential component that often goes unnoticed but plays a critical role in ensuring safety, durability, and efficiency. These gratings serve as protective covers over drainage systems, trenches, and ditches, facilitating proper water drainage while preventing unauthorized access and ensuring the safety of pedestrians and vehicular traffic.
Understanding Ditch Cover Steel Grating
Ditch cover steel grating is essentially a grid-like structure, typically made from steel, that covers open ditches and drainage systems. The design involves spatial configurations of bars or slats that allow water to flow through while supporting significant weight from passing vehicles. This structural component is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of drainage systems by preventing debris and other obstructions from entering the water pathways.
Advantages of Using Steel Grating
One of the primary reasons for choosing steel grating over alternative materials such as wood or plastic is durability. Steel has a higher load-bearing capacity, making it an ideal choice for areas with heavy foot and vehicular traffic. Additionally, steel is resistant to the elements, which means that it can withstand harsh weather conditions, including heavy rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. This longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, leading to lower maintenance costs for municipalities and property owners alike.
Another advantage of ditch cover steel grating is its versatility. It can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes to suit different applications, from residential driveways to industrial sites. Furthermore, steel gratings can be customized with different finishes, coatings, and designs that enhance aesthetic appeal while ensuring functionality. This adaptability makes steel grating suitable for a broad range of contexts, including urban infrastructure, parks, and commercial developments.
ditch cover steel grating
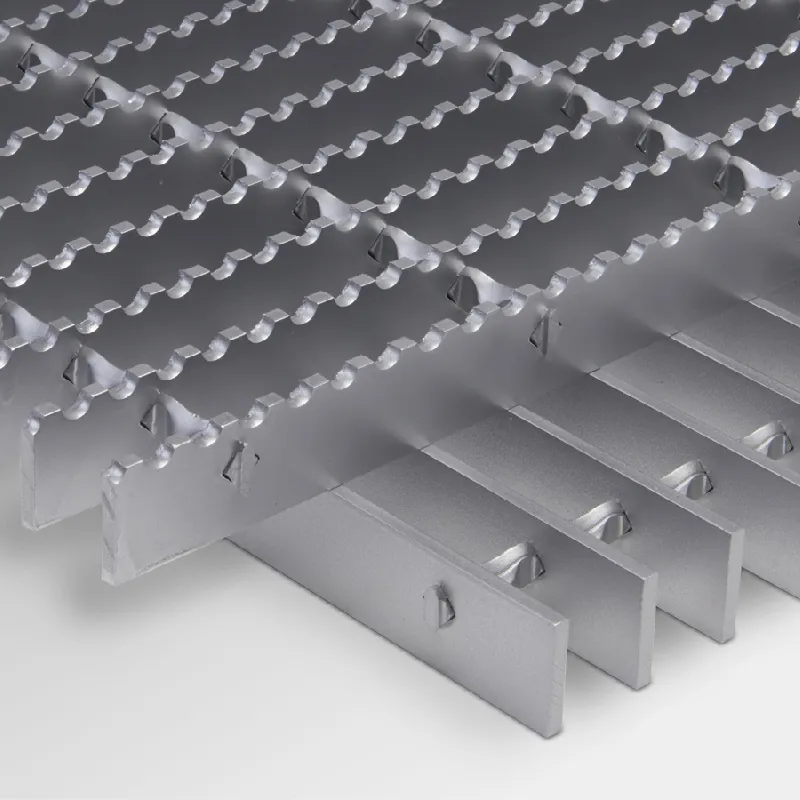
Safety and Accessibility
Safety is a paramount concern in public infrastructure. Ditch cover steel gratings are designed with safety features that mitigate risks for pedestrians and vehicles. The grating’s non-slip surface provides better traction, reducing the likelihood of slip-and-fall accidents, especially in wet conditions. Additionally, the open design of the grating allows for efficient water drainage, preventing the accumulation of water that could lead to hazardous situations.
Moreover, ditch cover steel grating can be engineered to comply with accessibility standards, ensuring that they are safe and usable for people with disabilities. Incorporating features such as gentle slopes and textured surfaces can enhance accessibility, enabling everyone to navigate public spaces comfortably.
Environmental Considerations
As environmental awareness grows, there is an increasing demand for sustainable building materials. Steel is a highly recyclable material, and many manufacturers employ eco-friendly practices in the production of steel grating. By choosing ditch cover steel grating, municipalities and developers can positively impact their environmental footprint. Furthermore, proper drainage facilitated by steel gratings can help prevent erosion, protect surrounding ecosystems, and promote responsible water management practices.
Conclusion
Ditch cover steel grating may seem like a minor detail in the larger picture of infrastructure development, but its importance cannot be overstated. By providing durability, safety, and versatility, these gratings play a crucial role in ensuring efficient drainage, reducing maintenance costs, and enhancing the overall safety of public and private spaces. As we continue to build and improve our urban environments, the integration of such reliable materials will be vital in creating sustainable and safe infrastructure for future generations. Whether for a residential application or a large-scale urban project, ditch cover steel grating is undoubtedly a fundamental element in modern construction practices.
-
Welded Steel Bar Grating: The Rugged Industrial Flooring Solution Built for Load and LongevityNewsJun.24,2025
-
Steel Walkway Grating: Reliable, Resilient, and Built for Every StepNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shale Shaker Screen for Sale: Optimize Drilling Efficiency with Precision Screening PowerNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shaker Screen for Sale: Elevate Your Drilling Efficiency with Durable Separation SolutionsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Press Locked Steel Grating: Industrial Strength with Precision Fit for Heavy-Duty ApplicationsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Perimeter Safety Netting: The Critical Safety Upgrade for Every HelipadNewsJun.24,2025