- Industrial zone, South of Anping Town, Hengshui, Hebei, China.
- sales@hfpetromesh.com
- +86-18931809706
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Exploring the Characteristics of 19% Weight for Four Grating Samples
Understanding 19% W 4 Grating Weight A Comprehensive Overview
In today's fast-paced industrial landscape, the effective management of materials is critical for optimizing production and ensuring safety. Among the numerous specifications and standards in material science, the term 19% W 4 grating weight has emerged as a focal point in the discussion of load-bearing structures and utility systems. This article aims to elucidate the significance of this specification and its practical implications in various applications.
Understanding 19% W 4 Grating Weight A Comprehensive Overview
The 4 in the term signifies a particular gauge or specification in the production of the grating. This could relate to the thickness or the pattern of the grating itself, dictating both its aesthetic appearance and functional utility. Gratings are generally produced in various forms—such as welded wire, bar grating, and expanded metal—to support diverse structural and environmental needs. The choice of grating design is crucial for determining load capacity, drainage efficiency, and accessibility.
19 w 4 grating weight
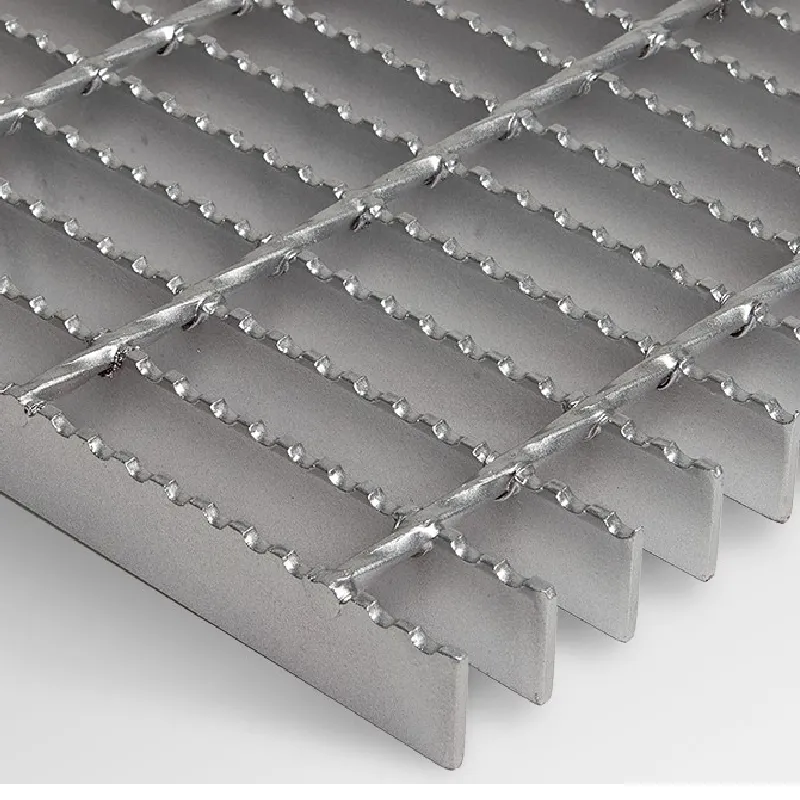
When discussing grating weight, it is essential to consider the implications for load-bearing applications. Grating weight is a critical factor in structural engineering, influencing the design process and the selection of materials. A heavier grating may offer enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity, while a lighter grating solution can reduce the overall weight of a construction project, thereby impacting cost-effectiveness and ease of installation.
In many industrial settings, including wastewater treatment plants and manufacturing facilities, the utilization of high-strength grating—such as those with a 19% tungsten composition—is vital. These grates not only support heavy machinery but also ensure safe passage for personnel and equipment. Their ability to withstand harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures further underscores their significance in specialized applications.
Moreover, using a specific percentage of tungsten can lead to innovations in design and methodology, paving the way for more advanced engineering solutions. For example, incorporating tungsten in grating systems can enhance their resistance to corrosion, thus extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs. This aspect is particularly relevant in environments where exposure to chemicals or weather conditions might weaken conventional materials.
Ultimately, understanding the implications of 19% W 4 grating weight extends beyond mere specifications; it involves an appreciation of how material science influences the safety, efficiency, and sustainability of industrial operations. As technology progresses and industries evolve, the importance of precise material composition and specifications will only continue to grow, ensuring that we can meet future demands with confidence and innovation.
-
Welded Steel Bar Grating: The Rugged Industrial Flooring Solution Built for Load and LongevityNewsJun.24,2025
-
Steel Walkway Grating: Reliable, Resilient, and Built for Every StepNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shale Shaker Screen for Sale: Optimize Drilling Efficiency with Precision Screening PowerNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shaker Screen for Sale: Elevate Your Drilling Efficiency with Durable Separation SolutionsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Press Locked Steel Grating: Industrial Strength with Precision Fit for Heavy-Duty ApplicationsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Perimeter Safety Netting: The Critical Safety Upgrade for Every HelipadNewsJun.24,2025