- Industrial zone, South of Anping Town, Hengshui, Hebei, China.
- sales@hfpetromesh.com
- +86-18931809706
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
2월 . 11, 2025 06:28
Back to list
grating types
Gratings are essential components in various industrial and architectural applications, known for their durability, versatility, and safety features. When discussing grating types, it's crucial to focus on the product's benefits and applications, enhancing our understanding of their practical implementations and material advantages. This comprehensive guide provides insights into different grating types, based on firsthand experience, expertise, and industry authority.
Plastic Gratings, typically composed of polyethylene or polypropylene, present an economical and lightweight option for applications requiring minimal structural strength. These types are predominantly used in non-load bearing installations, such as residential pools and patio areas. Their inherent resistance to moisture and chemicals makes them durable in wet environments, though they may not support heavy loads, emphasizing their role in light-duty applications. For practical applications, the choice of grating type hinges upon factors such as structural load requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints, demanding a profound understanding of each material's properties. This decision-making process benefits significantly from real-world testing and data-driven analysis, ensuring the grating chosen specifically supports and enhances operational efficiency. Beyond material types, various grating configurations, such as bar, riveted, or expanded gratings, also impact functionality and safety. Steel bar gratings are common in walkways and platforms due to their high load-bearing capacity and ease of installation. Riveted gratings, known for additional strength achieved by combining flat bars with cross bars, find critical applications in areas subject to substantial dynamic loads. Expanded gratings, crafted by stretching and slitting metal sheets, offer slip resistance and increased surface area, essential in slippery or hazardous environments. Given these considerations, selecting the right grating type involves more than examining physical properties. It requires insight into the specific environment, application demands, and lifecycle cost-benefit analysis. The authority and expertise of manufacturers and structural engineers play an integral role in guiding these decisions, affirming the importance of collaboration and consultation in achieving long-term safety and effectiveness. In conclusion, with each grating type presenting distinct advantages and limitations, it is imperative to align choices with the unique requirements of the application at hand. The evolution of grating materials and technologies continues to shape industrial landscapes, asserting the importance of continuous learning and adaptation in maintaining authoritative and reliable structures, ensuring the longevity and safety of installations across diverse environments.
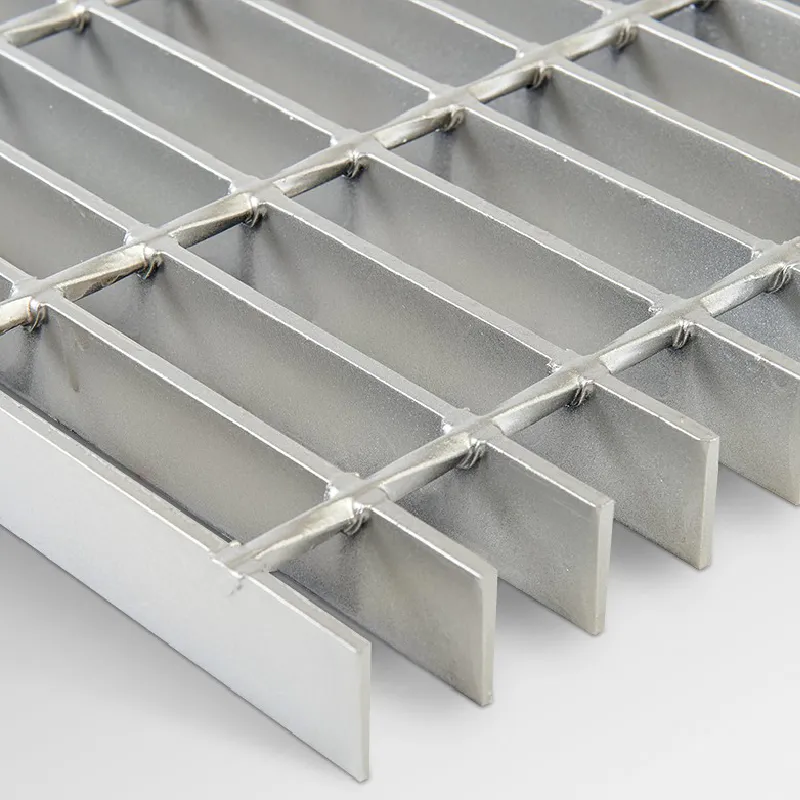
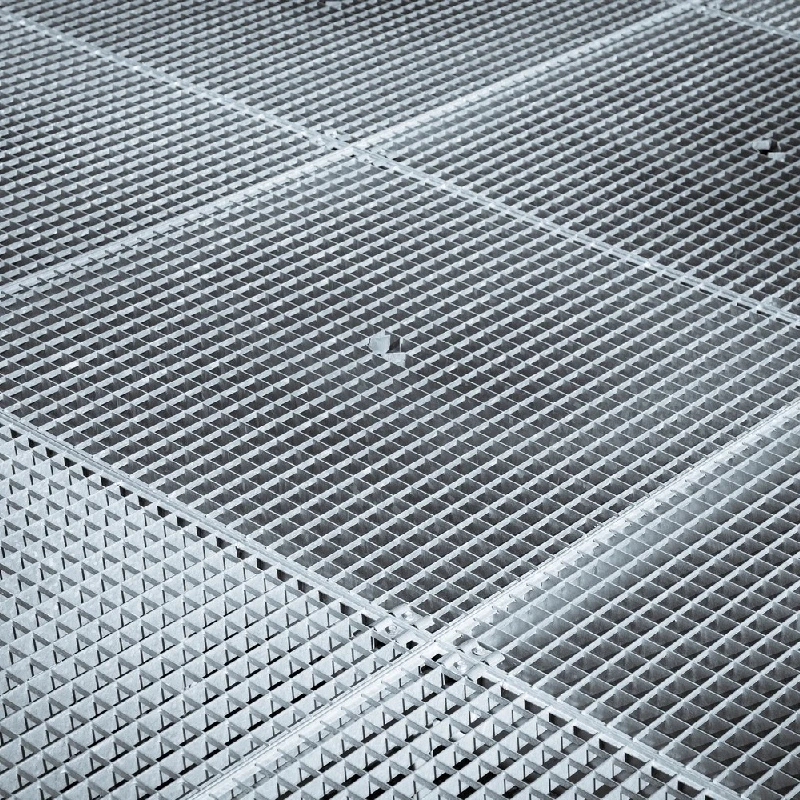
Plastic Gratings, typically composed of polyethylene or polypropylene, present an economical and lightweight option for applications requiring minimal structural strength. These types are predominantly used in non-load bearing installations, such as residential pools and patio areas. Their inherent resistance to moisture and chemicals makes them durable in wet environments, though they may not support heavy loads, emphasizing their role in light-duty applications. For practical applications, the choice of grating type hinges upon factors such as structural load requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints, demanding a profound understanding of each material's properties. This decision-making process benefits significantly from real-world testing and data-driven analysis, ensuring the grating chosen specifically supports and enhances operational efficiency. Beyond material types, various grating configurations, such as bar, riveted, or expanded gratings, also impact functionality and safety. Steel bar gratings are common in walkways and platforms due to their high load-bearing capacity and ease of installation. Riveted gratings, known for additional strength achieved by combining flat bars with cross bars, find critical applications in areas subject to substantial dynamic loads. Expanded gratings, crafted by stretching and slitting metal sheets, offer slip resistance and increased surface area, essential in slippery or hazardous environments. Given these considerations, selecting the right grating type involves more than examining physical properties. It requires insight into the specific environment, application demands, and lifecycle cost-benefit analysis. The authority and expertise of manufacturers and structural engineers play an integral role in guiding these decisions, affirming the importance of collaboration and consultation in achieving long-term safety and effectiveness. In conclusion, with each grating type presenting distinct advantages and limitations, it is imperative to align choices with the unique requirements of the application at hand. The evolution of grating materials and technologies continues to shape industrial landscapes, asserting the importance of continuous learning and adaptation in maintaining authoritative and reliable structures, ensuring the longevity and safety of installations across diverse environments.
Share
Prev:
Next:
Latest news
-
Welded Steel Bar Grating: The Rugged Industrial Flooring Solution Built for Load and LongevityNewsJun.24,2025
-
Steel Walkway Grating: Reliable, Resilient, and Built for Every StepNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shale Shaker Screen for Sale: Optimize Drilling Efficiency with Precision Screening PowerNewsJun.24,2025
-
Shaker Screen for Sale: Elevate Your Drilling Efficiency with Durable Separation SolutionsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Press Locked Steel Grating: Industrial Strength with Precision Fit for Heavy-Duty ApplicationsNewsJun.24,2025
-
Perimeter Safety Netting: The Critical Safety Upgrade for Every HelipadNewsJun.24,2025