- Industrial zone, South of Anping Town, Hengshui, Hebei, China.
- sales@hfpetromesh.com
- +86-18931809706
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
serrated grating
Serrated Grating An Exploration of Functionality and Aesthetics in Modern Design
In the realm of architectural and industrial design, the importance of both functionality and aesthetics cannot be overstated. One of the elements that has gained considerable attention in recent years is the serrated grating. This design feature, characterized by its saw-tooth or zigzag pattern, offers a unique blend of practical benefits and visual appeal. Understanding the significance of serrated grating is crucial for architects, designers, and engineers as they navigate the complex intersection of form and function.
Design and Functional Advantages
Serrated grating is often used in various applications, from flooring and walkways to facades and coverings. Its signature design provides a range of advantages that enhance safety and usability. One of its most significant features is the slip-resistant surface. The serrated edges create additional friction, which is particularly valuable in wet or icy conditions. This characteristic makes serrated grating an ideal choice for outdoor environments, such as parks, bridges, and docks, where the risk of slipping can be a serious concern.
Moreover, the design allows for excellent drainage. The gaps created by the serrated pattern enable water, debris, and other materials to flow through, preventing the accumulation of water and reducing the likelihood of water pooling. This is particularly important in settings where water management is critical, such as industrial sites and public areas. Additionally, the open nature of serrated grating can aid in reducing weight compared to solid materials, making it easier to install and maintain.
Aesthetic Appeal
Beyond its functional benefits, serrated grating offers aesthetic opportunities that have captured the imagination of designers and architects. The distinct geometric pattern adds a modern touch to various structures, allowing for creative expression. Whether used as a flooring option or as part of a façade, serrated grating can introduce a dynamic visual element that engages observers and enhances the overall design narrative.
The interplay of light and shadow created by the serrated edges also contributes to its visual appeal. As sunlight hits the surface at different angles, it casts intricate shadows that can transform the perception of space. This changing dynamic can add depth to an otherwise flat surface, making serrated grating an exciting choice for contemporary architecture.
serrated grating
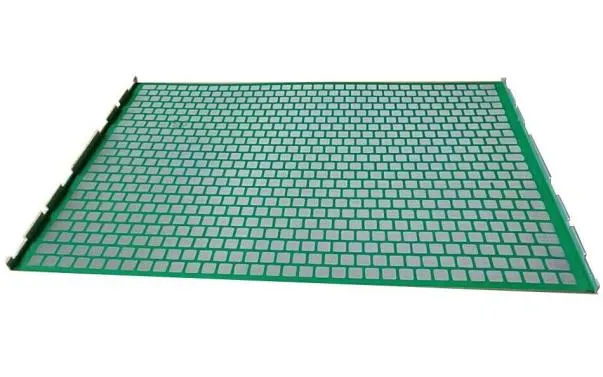
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of serrated grating extends across numerous industries. In industrial settings, it is utilized for walkways, platforms, and stair treads, providing safe access to machinery and equipment while maintaining structural integrity. In architectural applications, serrated grating can serve as cladding or screening, enhancing both the functional and aesthetic aspects of a building.
Moreover, serrated grating is gaining traction in the realm of sustainable design. Its ability to facilitate natural ventilation and daylighting can contribute to energy efficiency in buildings. Designers are increasingly incorporating serrated grating into green roofs and walls, allowing for plant growth while also permitting water drainage—an invaluable feature in sustainable urban environments.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many advantages, the use of serrated grating is not without challenges. One of the primary concerns is the maintenance of the material. Depending on the environment, serrated grating can accumulate dirt and debris in the depressions, requiring regular cleaning to maintain its functionality and appearance. Additionally, while the design is meant to be slip-resistant, periodic inspections are necessary to ensure that the surface remains safe for users.
Another consideration is the material choice for serrated grating. Various materials can be used, including metal, fiberglass, and plastic, each presenting its own set of advantages and challenges in terms of durability, cost, and environmental impact. Designers must carefully evaluate the specific requirements of their projects to select the most appropriate material.
Conclusion
Serrated grating stands at the intersection of functionality and aesthetics, offering unique benefits for a variety of applications across different fields. Its slip-resistant properties, drainage capabilities, and visual intrigue make it an appealing choice for modern design. As the trends in architecture and industrial design continue to evolve, serrated grating will undoubtedly play a prominent role in shaping the spaces we inhabit, fostering a blend of safety and style that mirrors contemporary values and needs.
-
Why Our Shaker Screen for Sale Stands Out in Every ApplicationNewsAug.08,2025
-
Unmatched Efficiency with Premium Shale Shaker Screen TechnologyNewsAug.08,2025
-
Reliable, Durable, and Cost-Effective: Press Locked Steel Grating SolutionsNewsAug.08,2025
-
Precision Strength with Welded Steel Bar GratingNewsAug.08,2025
-
Perimeter Safety Netting: The High-Strength Shield for Elevated Safety SolutionsNewsAug.08,2025
-
Maximize Performance with Steel Walkway GratingNewsAug.08,2025